A prevalent digestive condition, lactose intolerance manifests in various ways, primarily, individuals suffering from this disorder experience digestive discomfort post-dairy product consumption. It is crucial to recognize symptoms of lactose intolerance for effective management and a potential boost in overall well-being.
1. Understanding the Basics of Lactose Intolerance
The body's inability to digest lactose, a sugar found in milk and dairy products, characterizes lactose intolerance. This condition can impact individuals of all age groups due to an insufficient amount of the enzyme known as lactase within their digestive systems. This enzyme is responsible for breaking down the aforementioned sugar. Consequently, symptoms such as bloating, diarrhea, and even abdominal pain may serve as indicators of this condition.
Individuals suffering from lactose intolerance, in addition to digestive discomfort, may encounter fatigue because of nutrient malabsorption. Undigested lactose fermenting within the colon disrupts the gut bacteria balance. This disruption impacts essential vitamin and mineral absorption. Consequently, decreasing energy levels and instigating a pervasive sense of lethargy. Thus, recognizing and managing lactose intolerance becomes crucial for optimum well-being.
- Dietary Consideration: Consuming lactose-free products not only aids in symptom relief but also ensures better nutrient absorption, addressing potential fatigue associated with lactose intolerance.
- Lactose Tolerance Varies: The severity of lactose intolerance can vary among individuals, with some being more tolerant of small amounts of lactose than others.
2. Identifying Dairy Intolerance Signs
Subtle or pronounced, signs of dairy intolerance manifest differently in individuals. Nausea, flatulence, and stomach cramps often follow the consumption of dairy. These are common indicators. Accurate identification proves essential to distinguish these symptoms from other digestive issues. It enables appropriate dietary adjustments and effective symptom management.
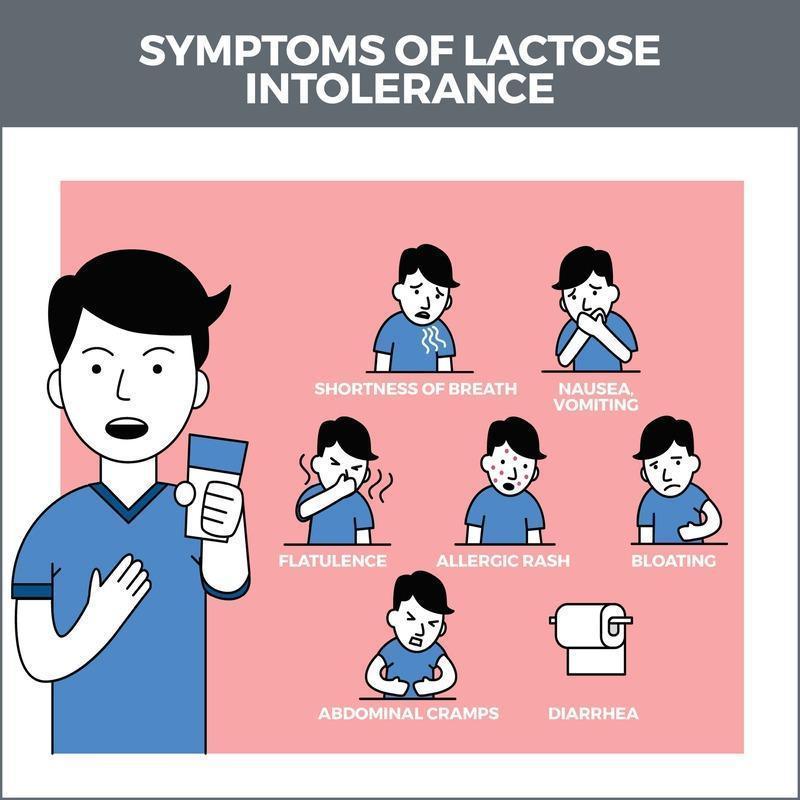
Grasping the fine distinctions of signs indicating dairy intolerance is pivotal for intervening promptly. Symptoms might not immediately appear after dairy consumption in certain instances, thereby posing a challenge to identify the cause accurately. The onset delay of symptoms, occurring hours later, could potentially convolute this identification process and result in extended discomfort. Maintaining a detailed food diary therefore aids in identifying patterns and ensures a more accurate assessment of signs related to dairy intolerance, maintaining a detailed food diary can aid in identifying patterns and ensuring a more accurate assessment of dairy intolerance signs.
- Caution: Dairy intolerance symptoms may overlap with other gastrointestinal conditions, emphasizing the need for a comprehensive assessment by a healthcare professional.
- Hydration Importance: Managing symptoms like diarrhea associated with dairy intolerance requires increased attention to hydration to prevent dehydration.
3. Navigating Lactose Intolerance in Daily Life
Individuals manage lactose intolerance by adopting dietary strategies. They often seek relief in the form of lactose-free alternatives such as dairy-free products and specifically, milk. Moreover, probiotics can facilitate digestion, providing a supportive measure to reduce symptoms and improve overall gut health.
Dietary adjustments pivotally contribute to managing symptoms, but lifestyle modifications can amplify this effect. Associations exist between regular physical activity and enhanced digestion. Overall well-being is also a contribution from it. By engaging in moderate exercise like walking or yoga, you can foster a holistic approach towards navigating lactose intolerance in daily life alongside dietary changes.
- Probiotic Diversity: Incorporating a variety of probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt with live cultures and fermented foods, supports the diversity of gut microbiota for better digestive health.
- Label Scrutiny: Careful examination of food labels is essential to identify hidden sources of lactose in processed and packaged foods.
4. Exploring Alternative Nutritional Sources
Individuals with lactose intolerance need not compromise on essential nutrients. They can obtain crucial calcium for bone health from non-dairy sources such as leafy greens, fortified cereals, and certain fish. Knowing about these alternative nutritional sources empowers individuals to maintain a well-balanced diet independently of dairy.
Incorporating sources of Vitamin D becomes imperative for maintaining bone health, in addition to calcium-rich alternatives such as exposure to sunlight, fortified foods, and dietary supplements. All provide necessary levels of Vitamin D. This ensures a comprehensive nutritional approach not just for individuals without lactose intolerance but particularly for those with it.
- Nutrient Synergy: Pairing calcium-rich foods with vitamin D sources enhances nutrient absorption, promoting optimal bone health.
- Plant-Based Protein: Non-dairy protein sources like beans, lentils, and tofu offer alternatives for individuals with lactose intolerance, supporting muscle health.
5. Seeking Professional Guidance for Lactose Intolerance

Consult a healthcare professional when experiencing persistent or severe symptoms. Diagnostic tests, conducted by a healthcare provider, confirm lactose intolerance and they provide personalized advice on dietary choices along with symptom management. Seek expert guidance for an accurate diagnosis and tailored solutions. This is crucial.
Professional guidance extends beyond providing symptomatic relief. It ensures a thorough understanding of individual health needs. Through regular monitoring, including periodic assessments of nutrient levels and digestive health, adjustments to the management plan can be made as necessary. A collaborative approach with healthcare providers not only guarantees comprehensive care but also addresses any emerging health concerns associated with lactose intolerance. Thus, fostering an environment where optimal well-being flourishes.
- Nutritional Counseling: Healthcare professionals, including dietitians, can provide tailored nutritional guidance to meet individual dietary needs and preferences.
- Long-Term Management: Lactose intolerance management involves long-term considerations, necessitating periodic health check-ups to address evolving health needs.
Conclusion
To wrap it all up, it is pivotal to recognize the symptoms of lactose intolerance for effective management. Understanding these signs of dairy intolerance empowers individuals. This recognition enables informed choices that alleviate symptoms and maintain a healthy and well-balanced lifestyle. Thus, navigating through the challenges imposed by lactose intolerance becomes more manageable. Dietary adjustments and exploration of alternative nutritional sources are essential in managing their condition effectively for those grappling with lactose intolerance. This process empowers them to take control over their health journey. Seeking professional guidance ensures accurate diagnosis and personalized solutions for optimal health. Use this detailed knowledge about lactose intolerance, manage your day-to-day dietary choices, and live a relaxed life.







